What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is a complication of diabetes that affects the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive layer at the back of your eye. High blood sugar levels can damage these vessels over time, leading to vision problems or even blindness if untreated.
Stages of DR:
-
Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR): Early stage where blood vessels weaken, leak fluid or blood, or form small bulges (microaneurysms). Vision may still be normal at this point.
-
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR): Advanced stage where new, fragile blood vessels grow on the retina or optic disc, potentially leading to severe vision loss from bleeding or retinal detachment.
Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy: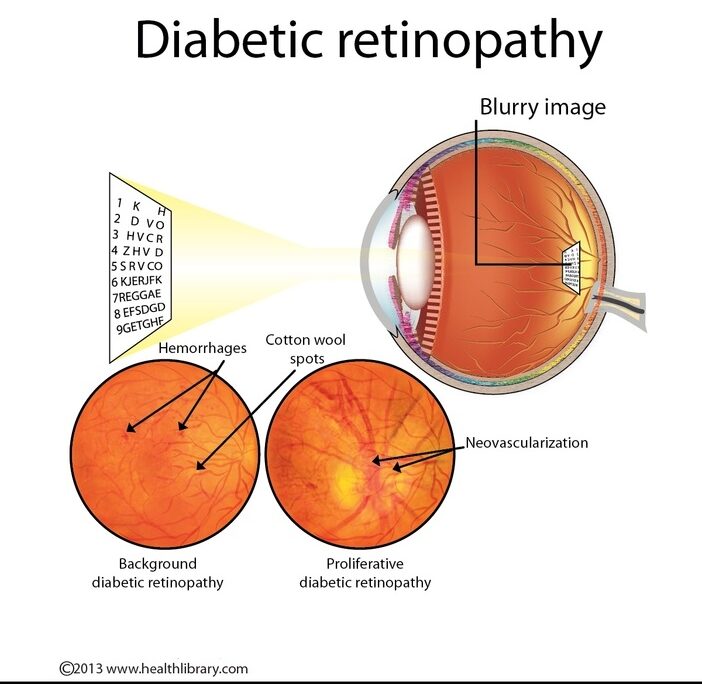
-
Often no symptoms in early stages
-
Blurred or fluctuating vision
-
Dark spots or floaters in your field of vision
-
Difficulty seeing at night
-
Loss of central vision
-
Colors appearing faded or washed out
Risk Factors:
-
Duration of diabetes (longer duration increases risk)
-
Poor blood sugar control
-
High blood pressure
-
High cholesterol
-
Kidney disease
-
Smoking
-
Pregnancy (in diabetic women)
Diagnosis:
We use advanced tools to detect DR:
-
Dilated Eye Exam: Allows a detailed view of the retina to spot swelling, leaks, or abnormal blood vessels.
-
Fundus Photography: Captures detailed images of the retina for monitoring progression.
-
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): Provides cross-sectional images to detect retinal swelling (macular edema).
-
Fluorescein Angiography: Uses dye to highlight blood vessel issues in severe cases.
Treatment: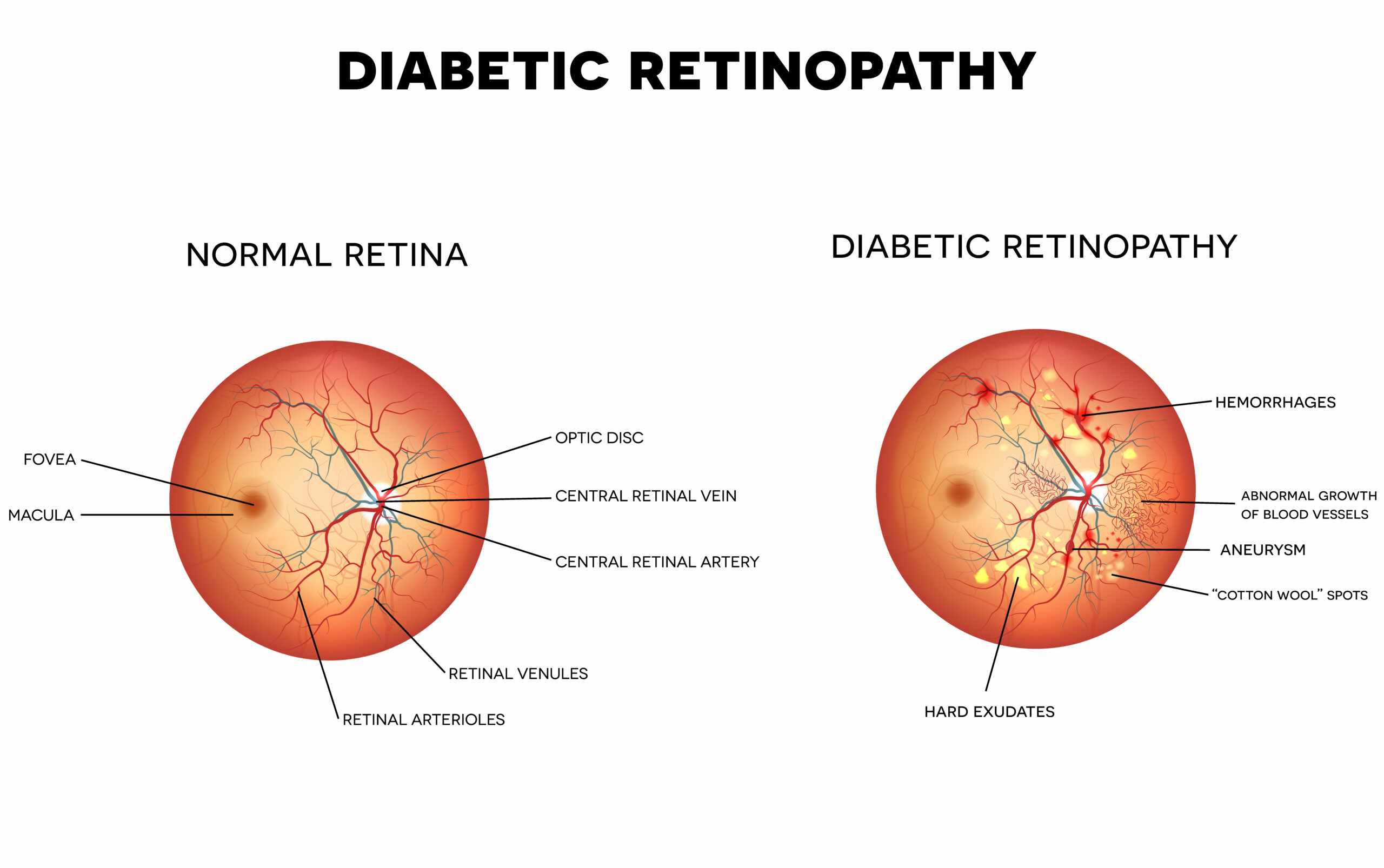
Early Stage (NPDR):
-
Strict blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol management.
-
Regular monitoring to prevent progression.
Advanced Stage (PDR or Macular Edema):
-
Laser Treatment (Photocoagulation): Seals leaking blood vessels or reduces abnormal vessel growth.
-
Anti-VEGF Injections: Reduces swelling and stops new vessel growth (e.g., Avastin, Lucentis).
-
Vitrectomy: Surgery to remove blood or scar tissue from the eye in severe cases.
Prevention and Management:
-
Maintain tight control of blood sugar levels with diet, exercise, and medication.
-
Regular eye exams (at least annually for diabetics, or more often if DR is present).
-
Manage blood pressure and cholesterol.
-
Quit smoking to improve circulation and reduce risk.
Why Choose Us?
-
Expertise in diabetic eye care with cutting-edge diagnostic technology.
-
Collaborative approach with your diabetes care team for holistic management.
-
Personalized treatment plans to preserve your vision.
